The procedures outlined in this guide are specifically for Windows systems. If you have a dual-boot/multiboot system with another operating system like Linux, these procedures could potentially make the non-Windows operating system unbootable.
Step-by-Step Guide
Prerequisites
You’ll need your Windows 10 installation media, such as a USB drive with a bootable Windows installation. Boot to the USB drive in Legacy BIOS mode.
Method 1: Using Command Prompt
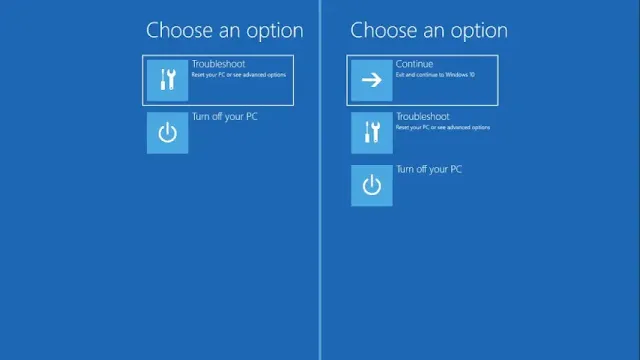
Access Command Prompt:
- Boot from your Windows installation media.
- Click on Next.
- Click on Repair My Computer.
- Click on Troubleshoot.
- Click on Command Prompt.
DiskPart Commands:
- Type diskpart and hit Enter.
- Type list disk and hit Enter.
- Identify the disk you want to convert (e.g., Disk 0).
- Type select disk 0 and hit Enter.
- Type list volume and hit Enter.
Identify Volumes:
- Locate the System Reserved Partition, which is usually around 50 to 100 MB in size. Note the volume number and letter (if available).
- Identify the primary partition where Windows is installed (e.g., Volume 1, Letter C for System Reserved; Volume 2, Letter D for Windows).
Select and Format System Reserved Partition:
- Type select volume 1 (replace 1 with your System Reserved volume number) and hit Enter.
- If the System Reserved Partition has no letter assigned, type assign letter=v (replace v with any unused letter) and hit Enter.
- Type list volume to confirm the System Reserved Partition is still selected and has a letter assigned.
- Type format fs=ntfs and hit Enter to format the partition.
Mark Partition as Active:
- Type active and hit Enter to mark the partition as active.
- Type exit and hit Enter to exit DiskPart.
Rebuild Boot Configuration Data (BCD):
- While still in the Command Prompt, type bcdboot d:\windows /s c: /f BIOS (replace D with your primary partition letter and C with your System Reserved partition letter) and hit Enter.
Finalize:
- Type exit and hit Enter to exit the Command Prompt.
- Turn off your PC, remove the USB drive, and turn it back on again.
Additional Commands for Boot Issues
If you encounter further issues, you may need to run additional commands in the Command Prompt:
- bootrec /fixMbr: Writes a new Windows-compatible Master Boot Record (MBR).
- bootrec /fixboot: Writes a new boot sector.
- bootrec /scanos: Scans for Windows installations not in the BCD store.
- bootrec /RebuildBcd: Rebuilds the BCD store.
- bootsect /nt60 SYS: Applies Bootmgr-compatible master boot code to the system partition.
- bootsect /nt60 ALL: Applies Bootmgr-compatible master boot code to all partitions.
- bcdboot d:\windows /s c: /f Both: Sets up the system partition to boot to Windows for both UEFI and BIOS.
These commands can help resolve various boot issues related to the MBR, boot sector, and BCD store.
By following these steps, you should be able to repair or rebuild your MBR System Reserved Partition and get your Windows system booting again.