Windows is one of the most widely used operating systems globally. However, many users still find themselves confused about the differences between x86 and x64, or 32-bit and 64-bit systems. Let’s dive into what these terms mean and how they impact your computer’s performance.
What Do x86 and x64 Mean?
The terms x86 and x64 refer to two types of instruction set architectures (ISA) developed by Intel and AMD. An ISA defines how software controls the CPU and specifies the behavior of machine code.
Originally, x86 referred to a family of ISAs that began with the Intel 8086 microprocessor. This line of processors became highly successful, and the term x86 was used to denote the 32-bit versions of these processors. When 64-bit processors were introduced, they were compatible with the x86 architecture and were referred to as x86-64 or AMD64, as AMD first introduced them. Intel later adopted this architecture and called it Intel 64. Over time, the terms were shortened to x64 for 64-bit and x86 for 32-bit.
Key Differences Between 32-bit and 64-bit (x86 vs x64)
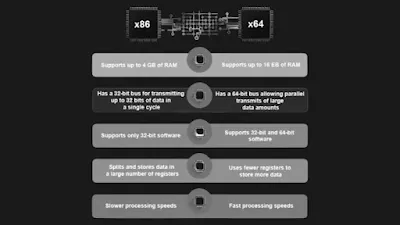
The most significant difference between 32-bit and 64-bit systems is the amount of RAM they can access. A 32-bit processor (x86) is limited to a maximum of 4 GB of physical memory, while a 64-bit processor (x64) can handle much larger amounts of memory, up to 16 exabytes (16 billion gigabytes).
Additionally, a 64-bit computer can run both 32-bit and 64-bit programs, whereas a 32-bit computer can only run 32-bit programs. This is due to the fundamental differences in their bit sizes. Modern laptops with pre-installed Windows are typically x64, while older computers might be x86.
In general, 64-bit processors are more efficient when dealing with large amounts of data. If you have a 64-bit Windows PC, you’ll notice a folder named “Program Files (x86)” on your C drive, which stores 32-bit applications. The “Program Files” folder, on the other hand, stores all the 64-bit apps you have installed.
How to Check if Your Windows Computer is 32-bit or 64-bit
To determine whether your Windows OS is 32-bit or 64-bit, follow these steps:
- Press the Win + X keys to open the context menu, and then click on “System”.
- In the pop-up window, navigate to the “System type” section under “Device specifications”. Here, you can see if your Windows OS is 32-bit or 64-bit.
Alternatively, you can use another simple method:
- Type msinfo32 in the search box and click on the “System Information” app.
- In the “System Summary” section, find the “System Type” on the right side. This will indicate whether your Windows OS is x64-based or not.